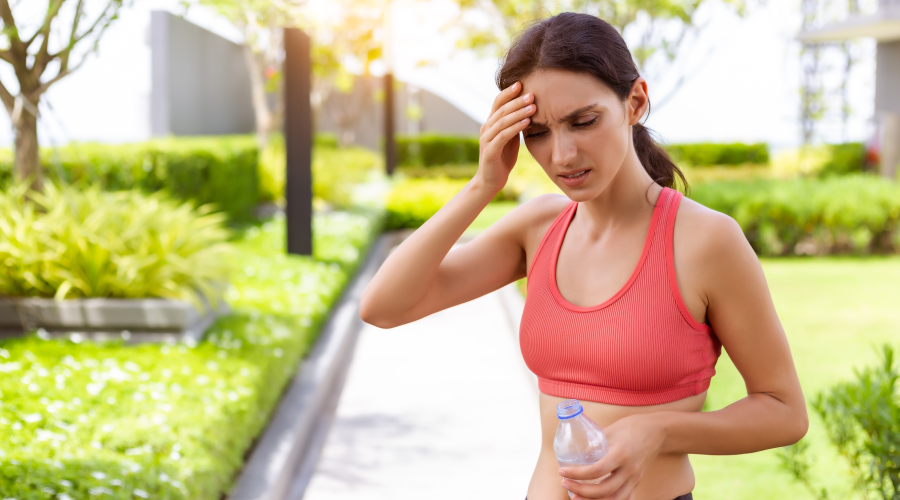
Dehydration is the imbalance between the actual fluid intake and what the body requires. When the body loses more fluid than what it takes in, it pushes the body into dehydration. Severe dehydration occurs when you fail to replace the lost fluids, which can eventually prove fatal. Read through to know about the causes of dehydration and important signs of dehydration you shouldn’t miss.
Causes of Dehydration
The body requires water for all biochemical reactions. It also eliminates the body’s toxic waste through sweat, breath, urine, and stools. An average adult human is required to drink 8-10 glasses of water every day. But dehydration occurs when the body uses or loses more water than what it takes in.

The most common causes of dehydration are:
- Fever – During high-grade fever, the body loses water through its skin to lower body temperature. This leads to fluid loss and dehydration.
- Vomiting and diarrhoea – Illnesses like diarrhoea and vomiting result in the expulsion of huge amounts of water from the body. This also disturbs the electrolyte balance.
- Excessive sweating – Sweating is the body’s mechanism to cool itself. Excessive sweating leads to fluid and electrolyte loss.
- Increased urination – The body removes toxic waste through urine. But certain medicines or chemical imbalances can cause an increase in urine output. This leads to excessive fluid loss which results in dehydration.
- Inadequate water intake – Some people are not in the habit of drinking water regularly. They drink water only when thirsty. As the fluid loss is not replenished, it leads to dehydration.
Common Signs of Dehydration
As the body begins to lose its water content, signs of dehydration begin to surface. The signs of dehydration differ with age.
The most common signs of dehydration in children are:
- Dry mouth
- Dry lips and tongue
- No wet diapers for three hours
- Less than six wet diapers per day
- No tears while crying
- Sunken soft spot on top of the skull
- Listlessness and irritability
- Sunken eyes
- Rapid breathing
- Cold hands and feet
- Dry, wrinkled skin
The most common signs of dehydration in adults are:
- Extreme thirst
- Reduced urination frequency
- Dark coloured urine
- Unexplained fatigue
- Dizziness and confusion
- Dry mouth
- Dry, shrivelled skin
- Cold hands and feet
- Headache
- Muscle cramps
- Rapid heartbeat with low blood pressure
- Rapid breathing
- Sunken eyes
- Irritability
- Fainting
- Loss of appetite
- Sugar craving
- Flushed skin
- Heat intolerance
- Constipation
Complications of Untreated Dehydration
Dehydration symptoms can range from mild to severe. Severe dehydration can become a medical emergency. Potential complications of untreated dehydration include:
- Heat Cramps – Dehydration in hot, humid conditions can trigger heat cramps. It is marked by acute muscle stiffness, dizziness, heavy sweating, and vomiting.
- Heat Exhaustion – When the body overheats in response to external factors, it leads to heat exhaustion. Drinking adequate water and staying in a cool environment helps.
- Heat Stroke – Heat exhaustion, if left untreated, can worsen into heat stroke. It requires immediate medical attention as it can prove fatal or cause lifelong complications.
- Seizures or mental confusion – Dehydration leads to low electrolyte count. The electrolyte imbalance brings about changes in the brain’s electrical activity. This can cause seizures which have both short and long-term effects on mental health and physical well-being.
- Reduced blood volume – Blood is more than 90% water. Dehydration causes the water concentration in the blood to decrease, making it thicker and difficult to move around. As blood carries oxygen to different parts of the body, reduced blood volume can spur life-threatening complications.

- Kidney failure – The kidneys filter the blood and remove toxins from the body through urination. Dehydration reduces the frequency of urination, restricting the elimination of toxins. As the toxic build-up in the body increases, it leads to kidney failure.
- Coma – Temporary or permanent disruption of the brain’s activity leads to coma, a prolonged state of unconsciousness. The brain becomes unresponsive to all stimuli. Comprehensive medical intervention is required to support organs until the person recovers from the coma.
Preventing Dehydration
The above discussion makes it evident that severe dehydration can prove to be life-threatening. Therefore, prevention of dehydration is the best way to stay protected. Helpful ways to prevent dehydration are:
- Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water every day even if you have a sedentary lifestyle.
- Increase water intake in case of fever or illness.
- Drink sufficient water if you have diarrhoea or vomiting. Seek medical advice in case you cannot hold fluids down.
- Drink plenty of water before and after sports or physical activity.
- Dress in comfortable clothes in the hot summer months.
- Avoid going out in hot sunlight. Drink sufficient water after every episode of profuse sweating.
Who is at Higher Risk of Dehydration?
While anyone who does not drink adequate water throughout the day can begin to develop signs of dehydration, dehydration is more likely to occur in some people:
- Infants and young children – Fever, diarrhoea, and vomiting can make young children lose high amounts of water. Moreover, it is sometimes difficult for the parents to understand if they’re infant is thirsty.
- Elderly – Older adults may not realise they are thirsty. Also, because of restricted movements, they may not drink sufficient water during the day.
- Ill health – People who are not feeling well may not want to get up and drink water.
- People on medications – People suffering from chronic diseases like diabetes and kidney conditions may be urinating more often due to their drug dose. Increased urination may lead to dehydration.
- Athletes – Physically active people may be losing more water and electrolytes through excessive sweating. Not drinking enough water after each workout session can lead to dehydration.
- People who are active outdoors – People who are engaged in outdoor activities or those who are required to commute in hot, humid weather may lose out on the water due to excessive sweating.
- Alcoholics – Alcohol is a diuretic. It leads to water loss from the body due to increased urination. People who consume high quantities of alcohol are at higher risk of dehydration.
Diagnosis of Dehydration
Given below are the different ways in which dehydration can be diagnosed:
1. Signs of Dehydration
A medical practitioner will diagnose dehydration based on physical signs and symptoms. However, to confirm the diagnosis and gauge the degree of dehydration, pharmacological assessment is mandatory. These include:
2. Blood Test
A blood test that checks for electrolytes helps confirm dehydration. Furthermore, blood tests for kidney function show how well the kidneys are functioning. These help ascertain the degree of dehydration.
3. Urine Analysis
Urine analysis can help ascertain the level of toxicity and dehydration in the body. It is also helpful for picking up signs of bladder infection.
Treatment of Dehydration
Treatment for dehydration revolves around replacing the lost fluids and maintaining the electrolyte balance. The method of fluid replenishment will, however, depend upon the age and severity of dehydration. The methods of rehydration are:
1. Oral
ORS, an oral rehydration solution, is a rehydration solution that contains water and salts in specific quantities that helps restore both fluid and electrolyte balance. ORS solution can be prepared at home or can be purchased over the counter from a pharmacy store.
2. Intravenous
Most adults with mild to moderate dehydration can recover well by simply increasing their fluid intake orally. However, treatment for severe dehydration will require delivering fluids and salts intravenously under medical supervision.
How to Prepare ORS at Home?
To make a rehydration solution at home, you’ll require the following:
- ½ tsp table salt
- 6 tsp sugar
- 1 litre water
It is important to note that while preparing ORS at home, it is important to use accurate measurements of salt, sugar and water. Also, the use of filtered water is recommended to eliminate water-based vectors.
Stir well till everything dissolves in water. In infants, begin by administering one tsp of the prepared solution every one to five minutes. Increase frequency if well tolerated.
Fluids to Avoid In Dehydration
While one may feel that drinking any kind of fluid may provide relief from dehydration. But this is not the case. Intake of certain fluids can worsen dehydration symptoms.
Therefore, the following fluids must be avoided during dehydration:
- Soda-based beverages
- Alcohol
- Caffeine drinks like coffee and tea
- Extra sweetened drinks
Conclusion
Dehydration happens when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. The loss of fluids can be because of illness, an active lifestyle, extreme weather conditions, or simply because of reduced water intake. But whatever the cause, the result can be extremely dangerous. It is therefore important to pick up early signs of dehydration which includes extreme thirst, reduced urination frequency, dark-coloured urine, dry mouth and headache.
If left untreated, signs of dehydration worsen quickly. Severe dehydration usually requires medical intervention as it can cause life-threatening complications and can also prove fatal.